√無料でダウンロード! sinus rhythm with 1st degree av block transitioning to ventricular paced rhythm 740243
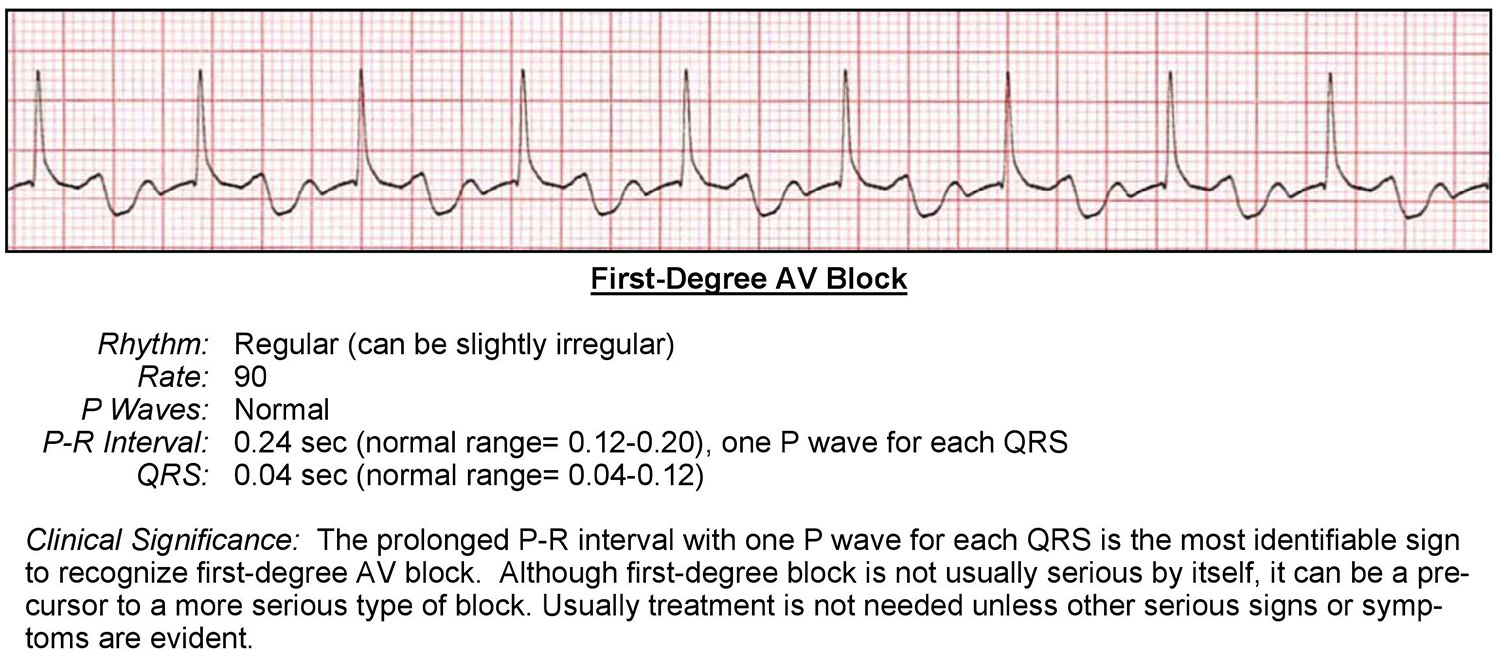
Sinus Rhythm means you heart is beating at a steady consistent rate A first degree AV block means that the electrical signal that starts in the Atria (upper chambers) of the heart and is relayed to the Ventricles (lower chambers) of the heart, is taking too long to get there It's sometimes referred to on the EKG as a prolonged PR timeFirst Degree AV Block ECG (Example 5) Second Degree AV Block Type I (Wenkebach) ECG (Example 1) Second Degree AV Block Type I (Wenkebach) ECG (Example 2) Second Degree AV Block Type I and 21 AVNo alert period or sensing capability (intrinsic Pwaves are ignored) Assumes AV conduction is intact (there is no heart block)
Year Old Male Cc Chest Pain Conclusion Ems 12 Lead
Sinus rhythm with 1st degree av block transitioning to ventricular paced rhythm
Sinus rhythm with 1st degree av block transitioning to ventricular paced rhythm-31/1/10 · Sinus bradycardia with first degree AV block Sinus bradycardia is evident from the long RR interval of 1280 ms, corresponding to a heart rate of 47 per minute PR interval is also prolonged at about 3 msec7/7/17 · Arrhythmias Arrhythmias are defined as disturbances in heart rate and/or conduction Arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse formation, abnormal impulse conduction, or both Arrhythmias may occur in children with normal hearts and/or may be associated with CHD, medications or electrolyte disturbances




First Degree Heart Block Acls Algorithms Com
Multiple and Consecutive PACs with Junctional Esca Sinus Rhythm with Run of Ventricular Tachycardia;Sinus rhythm (ie, activation of the atria from the SA node) can occur not only with normal (1 1) AV conduction but with any degree of AV heart block (including second or thirddegree), or even with ventricular tachycardia (a type of AV dissociation)Ventriculophasic sinus arrhythmia typically occurs in patients with sinus rhythm and complete AV block 1 2 3 In a complete AV block, differences may occur between PP intervals containing a QRS complex and intervals not containing a QRS The PP interval containing the QRS complex is shorter than the PP interval not containing the QRS complex
Sinus rhythm the normal rhythm of the heart A rhythm is defined as three consecutive heart beats with identical waveforms on the ECG The similarity of the waveforms indicates that the origin of the impulse is the same The sinoatrial (SA) node is the heart's pacemaker under normal circumstances and the rhythm is referred to as sinus rhythmHence, sinus rhythm is the normal rhythm1/8/18 · Atrial paced rhythm with 1st degree AV block There are regular pacing spikes at 90 bpm Each pacing spike is followed by a P wave, indicating 100% atrial capture P waves are conducted to the ventricles with a prolonged PR interval (280 ms)7 Bradycardia (sinus bradycardia, sinus arrest, SA block) 8 Tachyarrhythmias may be present (due to escape rhythms) 9 Implanted pacemaker 10 SA block 1 2 Next P wave appears where expected 11 Sinus arrest 1 2 Next P wave does not appear as expected (junctional escape beat) 3 AV Block 1 Firstdegree AV block 1 Delay in AV node 2
Hace 2 días · The PR interval is normally 01 seconds or 1 to 0 milliseconds A PR interval consistently longer than 0 seconds (greater than 5 small boxes) indicates a 1st degree AV block8/7/ · A sinus rhythm is any cardiac rhythm where depolarization of the heart muscle begins at the sinus node Normal sinus rhythm A normal sinus rhythm is considered the normal rhythm of a healthy heart, meaning the electrical pulse from the sinus node is exactly as expected A normal sinus rhythm is the one you'd prefer to see on every patient!Avb 2nd degree, mobitz i (wenckebach) av block 2nd degree, mobitz ii (hay) avb 2nd degree, 21 conduction;




Evaluation And Treatment Of Av Block And Intraventricular Conduction Disturbances The Cardiology Advisor



Hearts Free Full Text Cardiac Stimulation In The Third Millennium Where Do We Head From Here Html
· Ventricular paced 14 c Sinus arrest 15 a Sinus rhythm with PACs 16 d Demand ventricular pacing 17 a Atrial paced 18 a Third degree block 19 a Agonal rhythm a Atrial fibrillation 21 b Biventricular paced 22 c First degree block 23 d Sinus rhythm with quadrigeminal PVCs 24 a Sinus tachycardia 25 b Ventricular2nd Degree AV Block Mobitz Type II ♥Occurs when there is intermittent interruption of conduction ♥Less common that a 2nd Degree Type 1 block, but more dangerous ♥PR intervals are regular for conducted beats ♥The atrial rhythm is regular ♥The ventricular rhythm is irregular due to dropped or nonconducted (blocked) beatsNonconducted PACs or Sinus arrhythmia;



Ii Cardiology Radiology Key




Pdf Congenital And Childhood Atrioventricular Blocks Pathophysiology And Contemporary Management
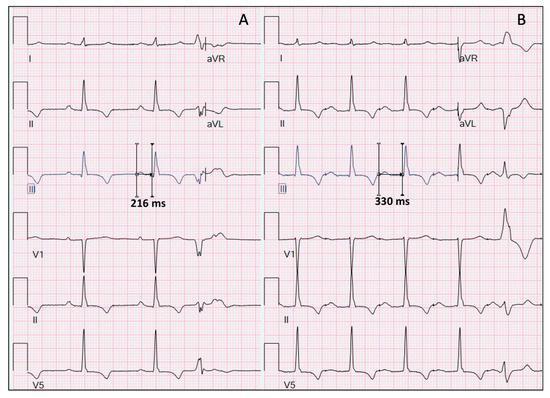
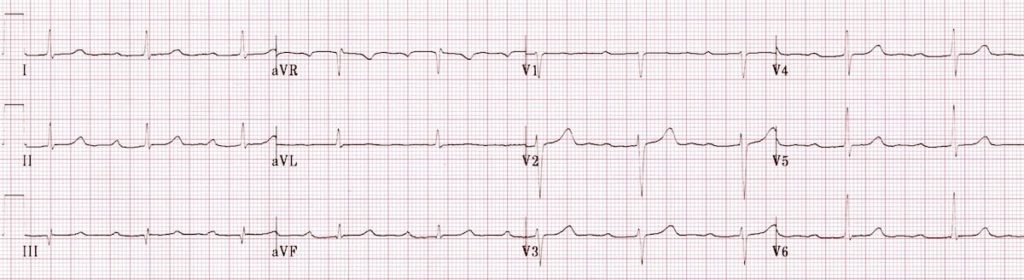
30/1/19 · This 12lead ECG tracing with rhythm strips shows consistent atrial and ventricular pacing at a rate of 71 bpm The atrial pacing stimulus outputs are followed by a prolonged AV interval (of 140 ms), after which the ventricle is paced from the right ventricle apex (apparent from the left bundle branch block pattern and the superior axis) · A first degree AVblock is said to be present when the PRinterval is greater than 0 ms in the setting of a sinus rhythm Figure 2 Sinus rhythm with first degree AVblock in a 16yo M s/p seizure The prolonged PRinterval is caused by a delay in conduction, usually within the AVnode but sometimes slightly above it in the atrial tissue or15/9/08 · Sandwiched in between these QRS complexes are nonconducting P waves This defines the rhythm as some type of 2nd degree AV block, since not all P waves are being conducted Of the three types of 2nd degree AV block, Mobitz Type I (or AV Wenckebach) is by far the most common




Arrhythmias



Features Ecgsimulator Net
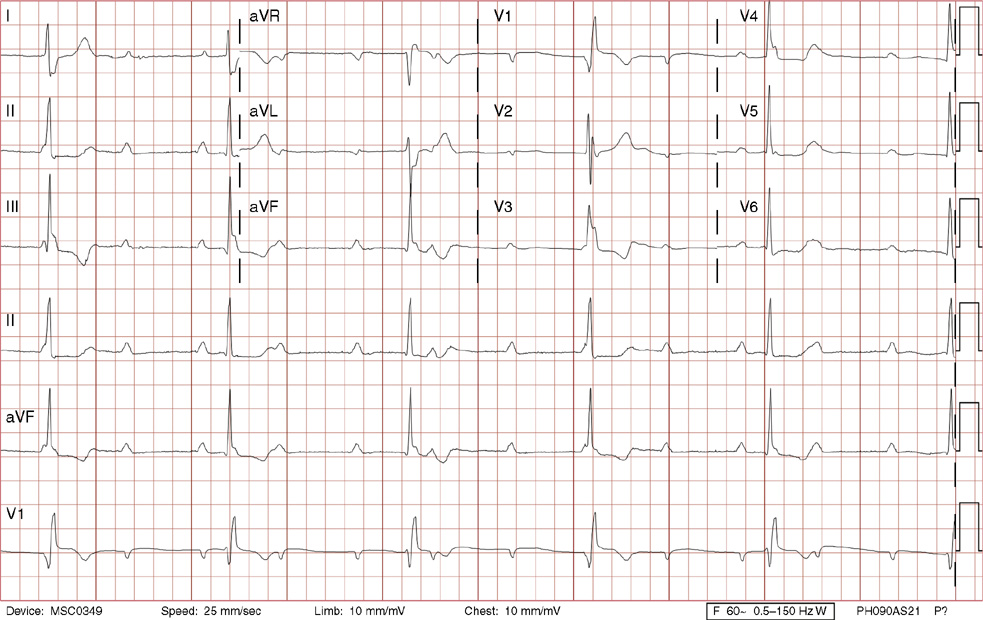
Rhythm analysis indicates normal sinus rhythm (NSR) with a 1st degree heart block This encounter displays a P wave of over 0 ms or one square away from the QRS, making it 1st degree heart block This condition represents a delay between atrial and ventricular conduction It is not considered dangerous, but can escalate to higher level blocks"with predominantly sinus rhythm, is just a short cycle of 2nd degree av block during a 48h holter ecg recording considered serious?" Answered by Dr Manjeet Singh Depends It depends on what type of 2nd degree AV block it was There9/1/17 · 1st degree block (7) 1st Degree Heart Blocks (2) 2nd degree block type I (30) 2nd degree block type II (26) 2nd Degree Heart Block Type I (2) 2nd Degree Heart Block Type II (3) 3rd degree block (31) Aberrancy (5) Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythms (18) Accelerated Junctional Rhythm (1) ACLS (240) ACLS pharmacology (29) ACLS questions () ACLS




Second Degree Av Block Acls Algorithms Com



Transitions Between Av Coupling Patterns At Changing Atrial Cycle Download Scientific Diagram
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators11/1/21 · Normal sinus rhythm with 1st degree block Monitor, ONLY if symptoms → Atropine Second Degree AV Block Type II Mobitz II Criteria Rhythm atrial is regular, ventricular is irregular PR constant no progressive lengthening P Not always followed by QRS QRS narrow high block wide low block PR interval is prolonged, but it is always the same TC pacing PacemakersSlow and wide junctional escape with bundle branch block vs ventricular escape rhythm Fast and narrow SVT Fast and wide probable ventricular tachycardia If rate is normal QRS narrow accelerated AV junctional rhythm (rare) sinus rhythm with 1st degree AV block ( search for Ps hidden in the preceding T) QRS wide



Www Mdpi Com 2673 3846 2 1 3 Pdf




Arrhythmias
Abnormal sinus rhythm Sick sinus rhythm Sinus node dysfunction also known by its historical name sick sinus syndrome or sinus node disease, is a group of heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias) in which the heart's natural pacemaker (sinoatrial node SA node) doesn't work properly to produce an adequate heart rate that meets the physiologic needs of the individual 2)Avb 2nd degree, "high grade av block" avb 3rd degree (complete heart block) avnrt (av nodal reentry tachycardia) avrt (av reentry tachycardia) brash syndrome;70 Normal Sinus Rhythm 71 Sinus Rhythm with 1st Degree AV block (PR 26 seconds) 72 Atrila Fibrillation (with a few flutter beats) 73 Juntional Rhythm (P waves occur after the QRS with HR 50) 74 2nd Degree AV Block Mobitz I (Wenchebach) PR gets longer, longer then dropped QRS




Hearts Free Full Text Cardiac Stimulation In The Third Millennium Where Do We Head From Here Html



First Degree Heart Block Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis
What is Sinus rhythm with 1st degreeAV block Septal infarct,age undetermined Abnormal ECG on Lab Report RBC438 Hemoglobin 138 They say I had a silent heart attack I had mild chest pain,especially if I pressed on it I was dizzy and somewhat disoriented,slurred some words and my cognitive function is slow now7/9/14 · Frequent ventricular premature complex 2 Lateral sign of ischemia This may be sign for severe cardiac problems If you were my patient I would suggest to do immediately ECHO Ecg Holter monitoring stress test Sinus rhythm with short pr, what does that mean on a ekgVentricular rhythm typically occurs during complete heart block (thirddegree AV block) Importantly, ventricular rhythm is not a reliable rhythm as it may cease working Figure 1 exemplifies a ventricular rhythm Accelerated ventricular rhythm (idioventricular rhythm) is a rhythm with rate at 60–100




Atrioventricular Block And Pause Dependent Torsade De Pointes Heartrhythm Case Reports



Management Of Refractory Arrhythmias In The Neurocritical Care Unit Chapter 27 Neurocritical Care
Ventricular Paced Rhythm Pacemaker not Captured AV Dual‐Paced 1st Degree AV Block 3rd Degree AV Block SinBrad SinPNC 2ºT1AVB 2ºT2AVB 2º21AVB Sinus Rhythm with Premature Nodal Contractions 2nd Degree Type I AV Block 2nd Degree Type II AV Block 2nd Degree 21 AV Block SinTach Sinus Tachycardia SinResp Sinus Respiratory Arrhythmia13/7/15 · Demand ventricular pacing (ventricles are paced when needed) Intrinsic Rwaves are sensed and inhibit ventricular output;5/7/12 · Ventricular premature complexes are a benign condition that can cause an irregular heartbeat It's very common, and many people will experience it



Lms Rn Com Getpdf Php 1804 Pdf



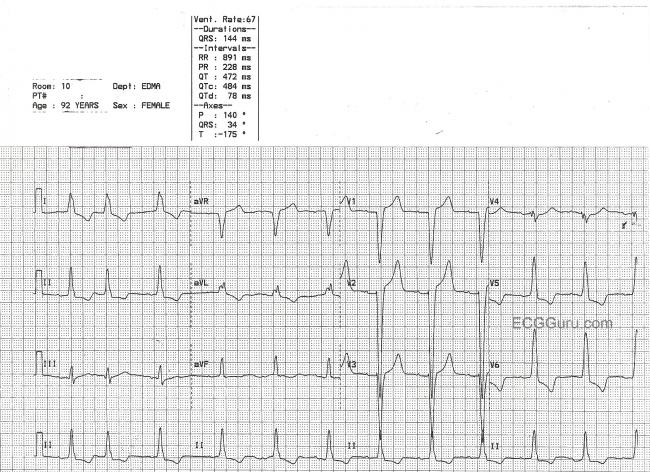
First And Second Degree Atrioventricular Block Thoracic Key
3/2/13 · Fusion can be described as an almost simultaneous sinus beat and ventricular beat The depolarization waves, one coming from the top of the heart and one coming from the bottom, meet and "fuse" on the ECG Fusion beats will have some characteristics of the supraventricular beats and some of the ventricular beats28/3/21 · Sinus bradycardia with 2nd degree type II c Complete (third degree) AV block 100% ventricular paced rhythm d) Sinus rhythm with ST elevation and first degree bloc In paced rhythm, much like left bundle branch block, the ST segments and T wave should be deflected opposite the majority of the QRS complex/3/21 · Premature ventricular complexes (PVCs), also known as premature ventricular contractions, ventricular premature beats (VPBs) or ventricular extrasystoles, are ectopic impulses originating from an area distal to the HisPurkinje system Premature ventricular complexes are the most common arrhythmia observed in patients without structural heart




Appropriate Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Therapies Delivered 5 Years After End Of Service Jacc Case Reports




His Bundle Pacing Sciencedirect
3rd Degree AV Block Rx'ed With a Ventricular Pacemaker Complete AV Block, Junctional Escape Rhythm, and Ventriculophasic Sinus Arrhythmia 2nd Degree AV Block, Type I, With Accelerated Junctional Escapes and a Ladder Diagram9/2/15 · 18 After admitting a patient and placing them on telemetry you interpret the rhythm as Sinus Bradycardia with a 1st Degree AV Block Your intial nurisng actions are to A Initiate CPR B Call a Rapid Response C Check the patient, find cause, and determine if this is patients baseline8/6/16 · Wiring of heart Sinus rhythm means that the electrical activity that controls the contraction of the heart, starts in the sinus node Right bundle branch block means that the right bundle (part of the electrical wiring) does not conduct the impulse which changes the appearance of the ekg Right bundle branch block as opposed to left bundle branch block is usually benign




Float Nurse Basic Ekg Rhythm Test 15



Ecg A Pictorial Primer
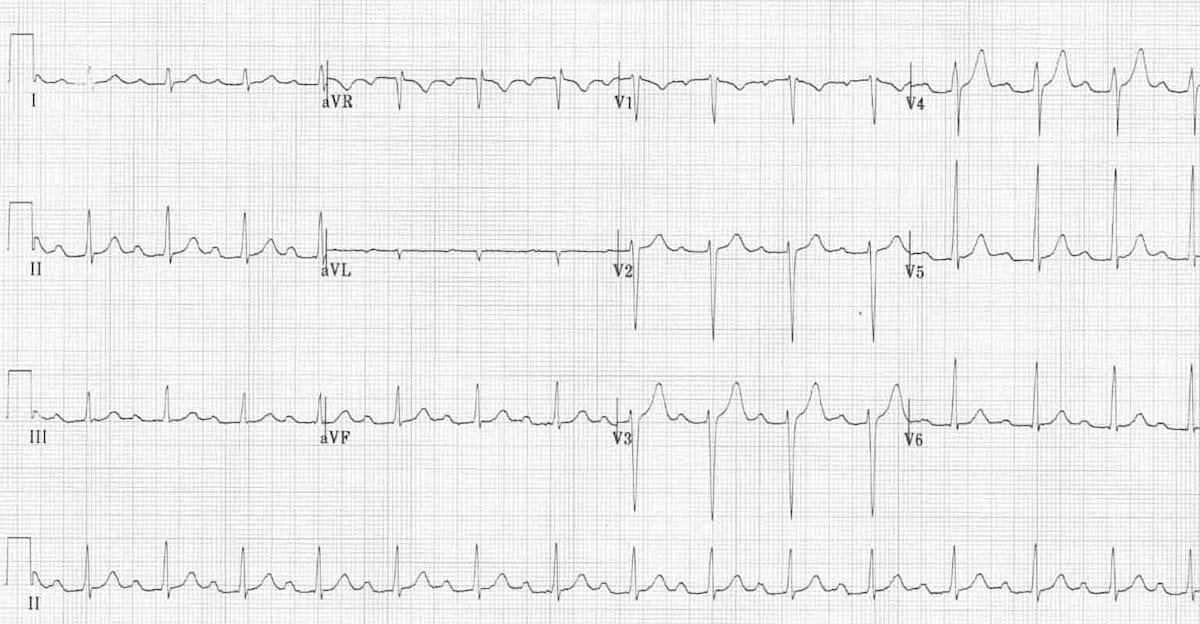
21/4/13 · Dawn presented "the basics" of this rhythm strip namely that there is marked sinus bradycardia and 1st degree AV block If one's audience consisted primarily of less experienced interpreters that might be as far as one goes ( with notable ADDITION of the obvious variability in RR interval that clearly satisfies a diagnosis of "sinus bradycardia and arrhythmia" )A Sinus Rhythm with PAC's B Junctional Rhythm C 2nd Degree AV Block, Type I D 3rd Degree AV Block E Normal Sinus Rhythm with PVC's F Idioventricular Rhythm9/10/16 · This 80something patient presented with chest pain He had recently had a pacer placed for complete heart block and had not had an angiogram at that time Ischemia had not been suspected There is sinus rhythm There is clearly a DDD pacer that detects the sinus activity and then paces the ventricle (necessary when there is complete AV block)




Hearts Free Full Text Cardiac Stimulation In The Third Millennium Where Do We Head From Here Html




Supplemental Materials For Troubleshooting And Programming Considerations For His Bundle Pacing Heart Rhythm
10/7/16 · First and SecondDegree Atrioventricular Block Fig 151 Sinus rhythm with a junctional premature beat (J), which results in AV node refractoriness and block of the next sinus beat *Subsequent nonconducted atrial impulse may be due to concealed junctional extrasystole, again making the AV node refractory without activating atrium or ventricleWhat does sinus rhythm with first degree av block moderate intraventricular conduction delay 110ms QRS duration mean Answered by a verified Doctor We use cookies to give you the best possible experience on our website22/4/16 · Sinus Rhythm with Ventricular Escape Beats;
.png)



Float Nurse Practice Ekg Strips 359




Supplemental Materials For Discriminating Electrocardiographic Responses To His Bundle Pacing Using Machine Learning Cardiovascular Digital Health Journal
Hi my ECG this week showed abnormal ECG Sinus rhythm with occasional premature ventricular complexes Inferior myocardial infarction 40* ms Q wave and or ST/T abnormality in II aVF1 probably old This is exactly how it's written, can anyone tell me a bit more about what this means, I do have regular very noticeable palpitationsSinus Bradycardia with Sinus Arrhythmia;AOO Atrial asynchronous pacing Continuous atrial pacing at a prescribed rate;




Arrhythmias
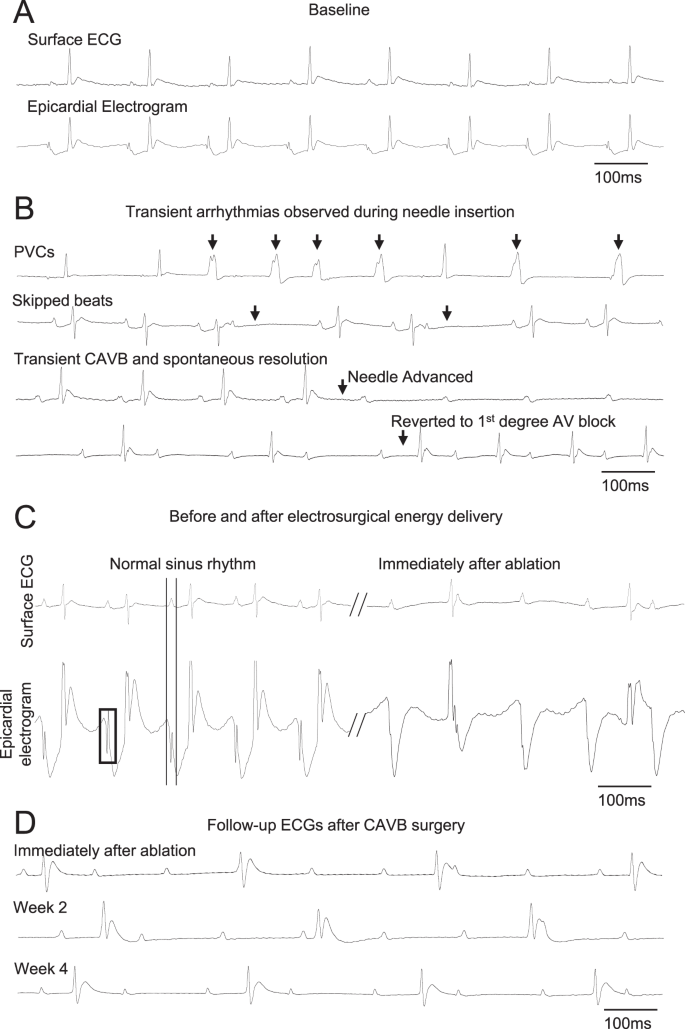



A Rat Model Of Complete Atrioventricular Block Recapitulates Clinical Indices Of Bradycardia And Provides A Platform To Test Disease Modifying Therapies Scientific Reports
Firstdegree atrioventricular block (AV block) is a disease of the electrical conduction system of the heart in which electrical impulses conduct from the cardiac atria to the ventricles through the atrioventricular node (AV node) more slowly than normal First degree AV block does not generally cause any symptoms, but may progress to more severe forms of heart block such as second2nd Degree Heart Block Type II;Firstdegree heart block, or firstdegree AV block, is when the electrical impulse moves through the AV node more slowly than normal The time it takes for the impulse to get from the atria to the



First Degree Heart Block Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Third Degree Av Block Example Learntheheart Com
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators



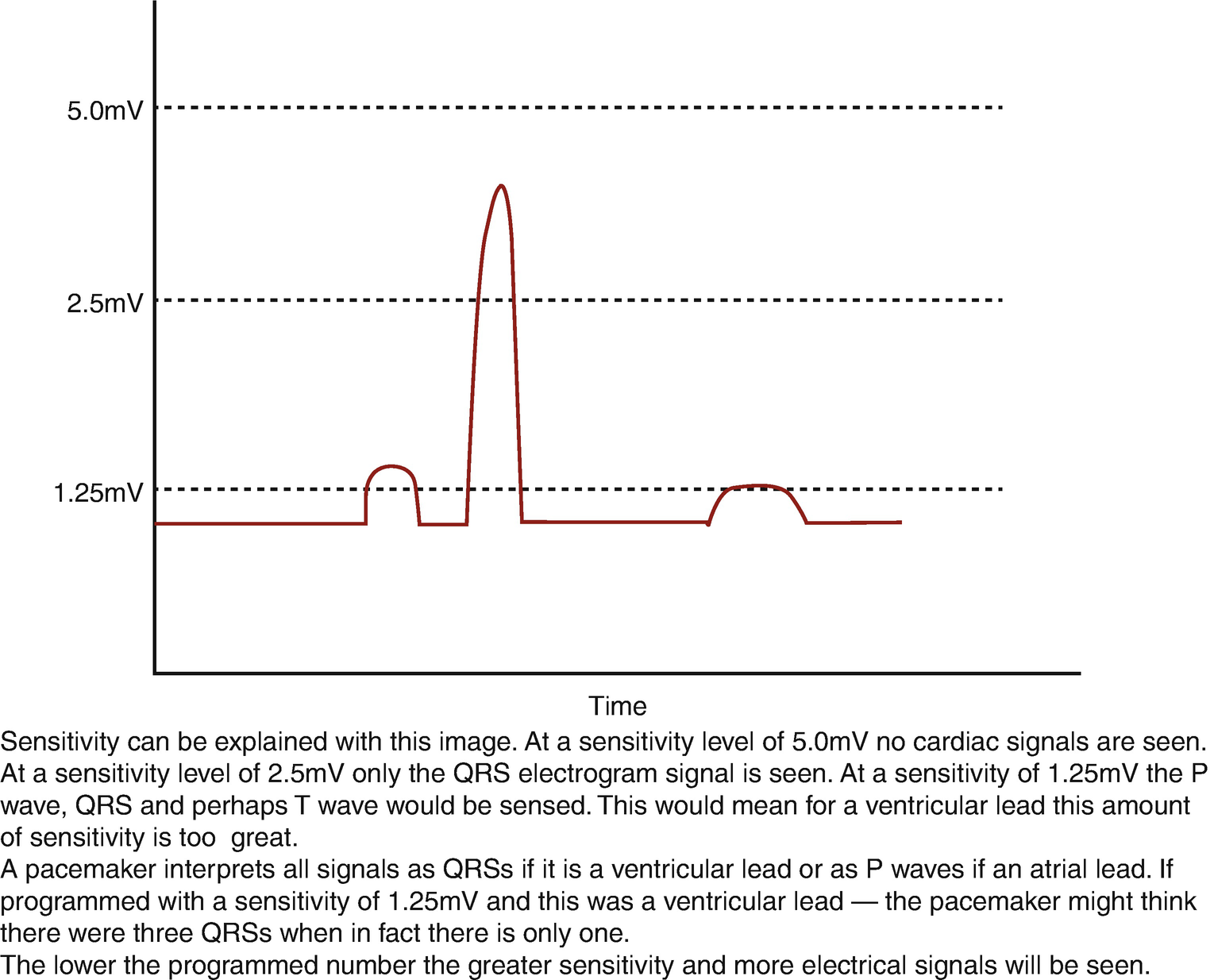
Atrioventricular Blocks Acls Wiki



Search Q Ventricular Paced Rhythm With Failure To Capture Tbm Isch



Cardiac Pacing In Adults Springerlink




First Degree Heart Block Acls Algorithms Com




Junctional Ectopic Tachycardia In Infants And Children Kylat Journal Of Arrhythmia Wiley Online Library




Novel Method For Assessment Of His Bundle Pacing Morphology Using Near Field And Far Field Device Electrograms Circulation Arrhythmia And Electrophysiology




Pacemaker Learntheheart Com
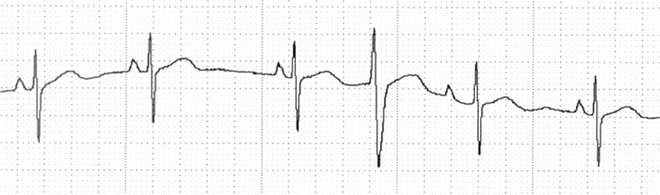



First And Second Degree Atrioventricular Block Thoracic Key




Left Bundle Branch Block Ecg 4 Learntheheart Com




Evaluation And Treatment Of Av Block And Intraventricular Conduction Disturbances The Cardiology Advisor




Pdf Congenital And Childhood Atrioventricular Blocks Pathophysiology And Contemporary Management




Intracardiac Electrocardiograms Demonstrating Pacemaker Dependence Download Scientific Diagram




The Canadian Cardiovascular Society Canadian Heart Rhythm Society Comprehensive Guidelines For The Management Of Atrial Fibrillation Canadian Journal Of Cardiology
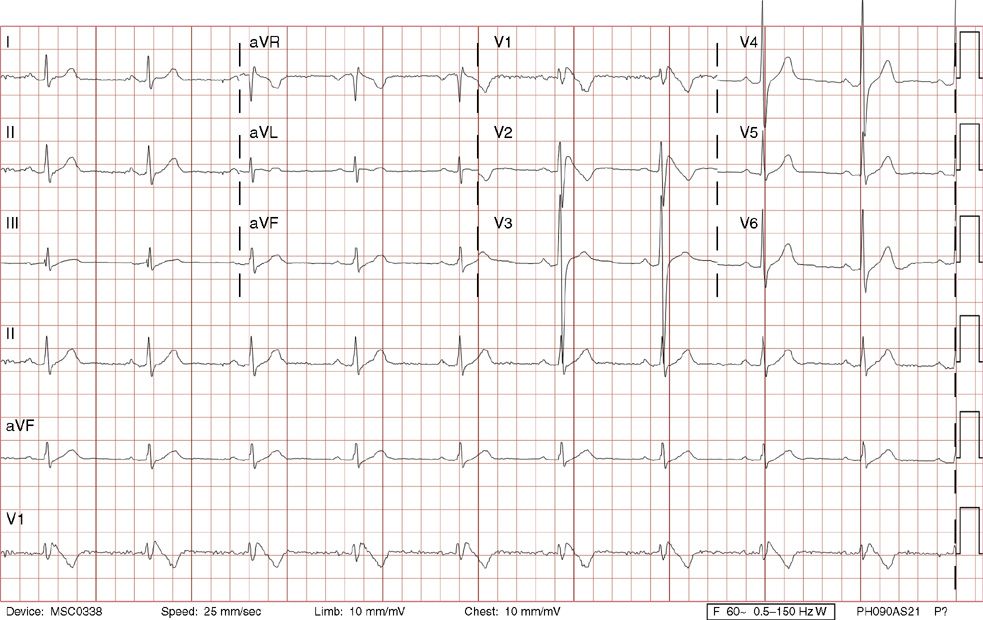



Ii Cardiology Radiology Key



Www Ahajournals Org Doi Pdf 10 1161 01 Cir 54 6 914




Cme Ecg S Flashcards Quizlet
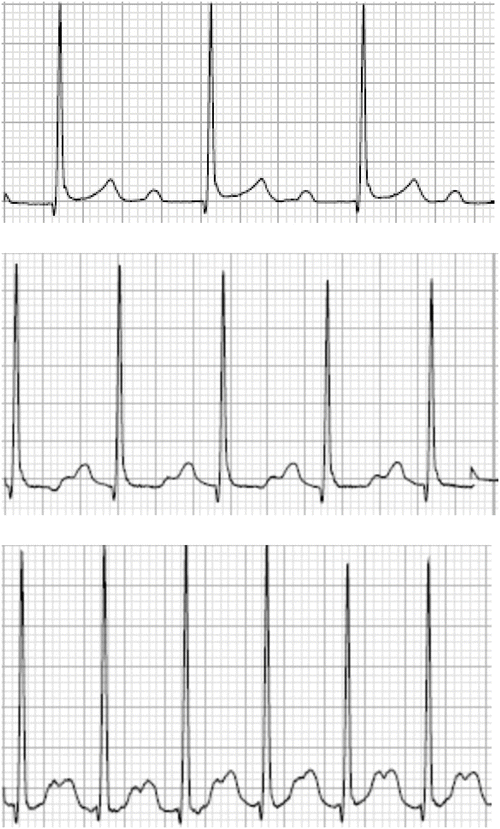



First And Second Degree Atrioventricular Block Thoracic Key
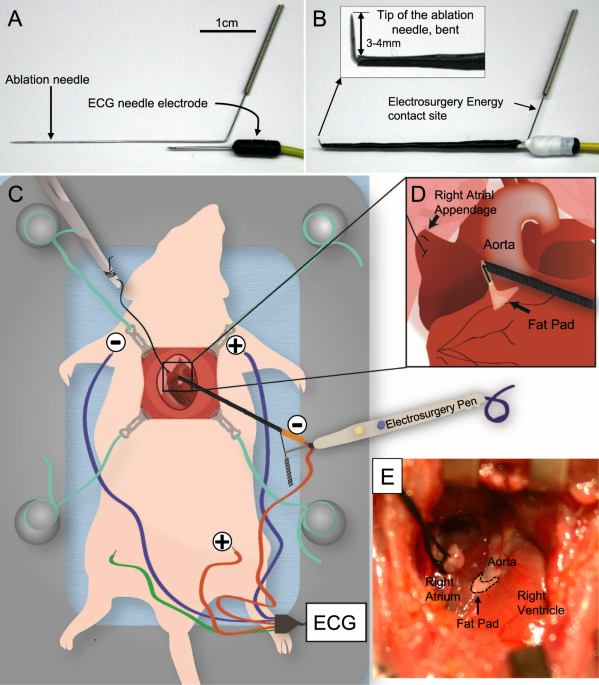



A Rat Model Of Complete Atrioventricular Block Recapitulates Clinical Indices Of Bradycardia And Provides A Platform To Test Disease Modifying Therapies Scientific Reports
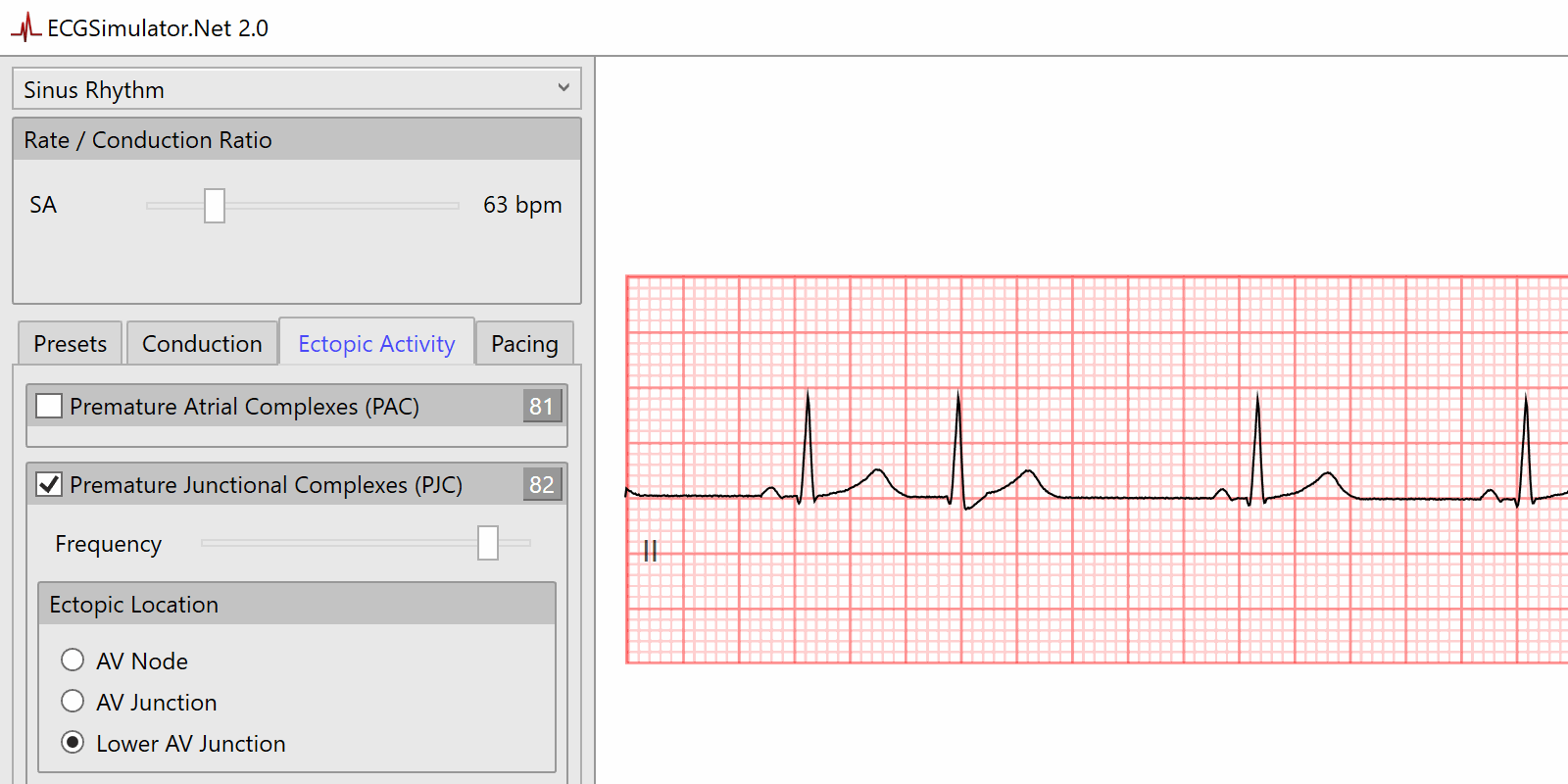



Features Ecgsimulator Net




Junctional Ectopic Tachycardia In Infants And Children Kylat Journal Of Arrhythmia Wiley Online Library




First And Second Degree Atrioventricular Block Thoracic Key



Lms Rn Com Getpdf Php 1804 Pdf
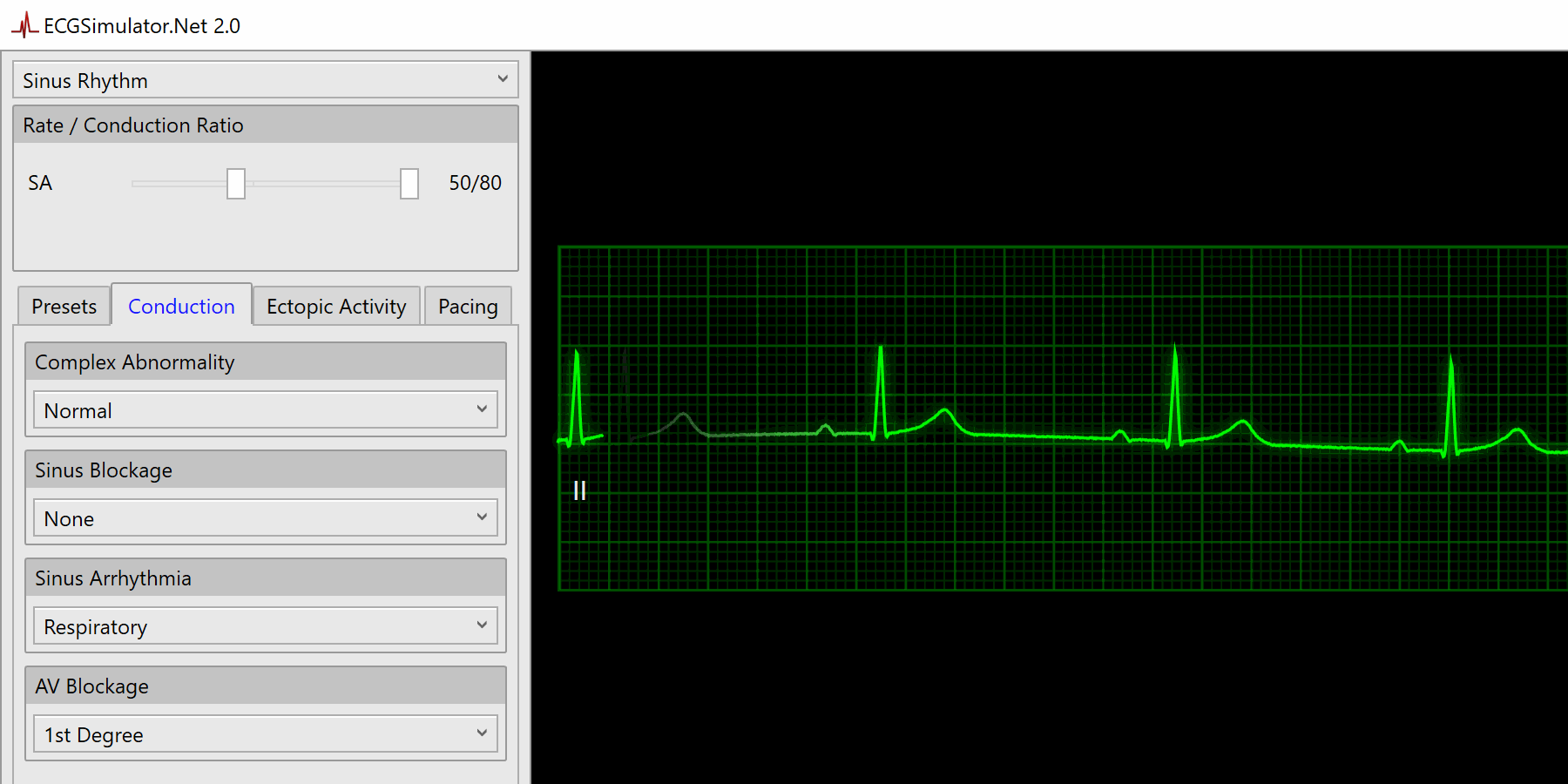



Features Ecgsimulator Net




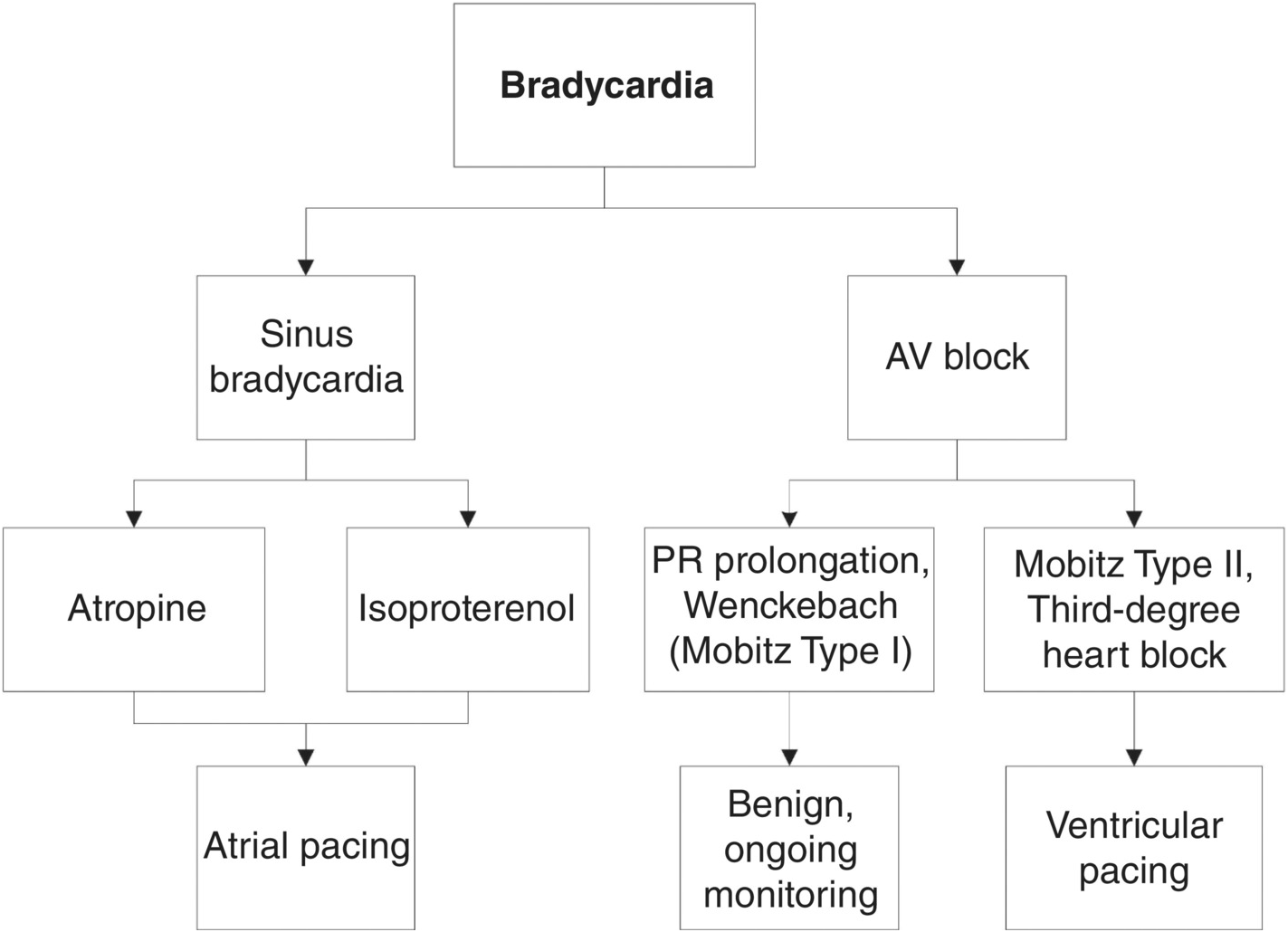
Bradycardia Emcrit Project




Electrocardiographic Analysis For His Bundle Pacing At Implantation And Follow Up Sciencedirect




Hearts Free Full Text Cardiac Stimulation In The Third Millennium Where Do We Head From Here Html




Hearts Free Full Text Cardiac Stimulation In The Third Millennium Where Do We Head From Here Html




New Generation Atrial Antitachycardia Pacing Reactive Atp Is Associated With Reduced Risk Of Persistent Or Permanent Atrial Fibrillation In Patients With Bradycardia Results From The Minerva Randomized Multicenter International Trial Heart Rhythm




Ectopic Atrial Rhythms Ecg Review Criteria And Examples Learntheheart Com




Electrocardiographic Analysis For His Bundle Pacing At Implantation And Follow Up Sciencedirect




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog A Patient With A Ventricular Paced Rhythm And Chest Pain




Within Patient Comparison Of His Bundle Pacing Right Ventricular Pacing And Right Ventricular Pacing Avoidance Algorithms In Patients With Pr Prolongation Acute Hemodynamic Study Keene Journal Of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology
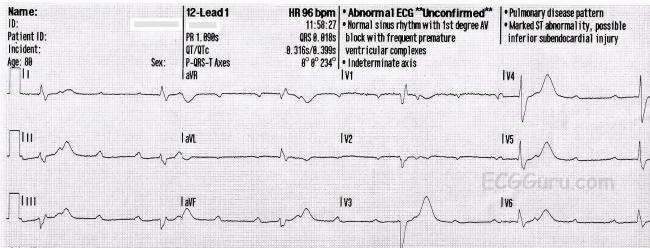



Av Block Ecg Guru Instructor Resources



Year Old Male Cc Chest Pain Conclusion Ems 12 Lead




Ventricular Bigeminy Ecg Example 1 Learntheheart Com




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog A Patient With A Ventricular Paced Rhythm And Chest Pain




Pdf Congenital And Childhood Atrioventricular Blocks Pathophysiology And Contemporary Management
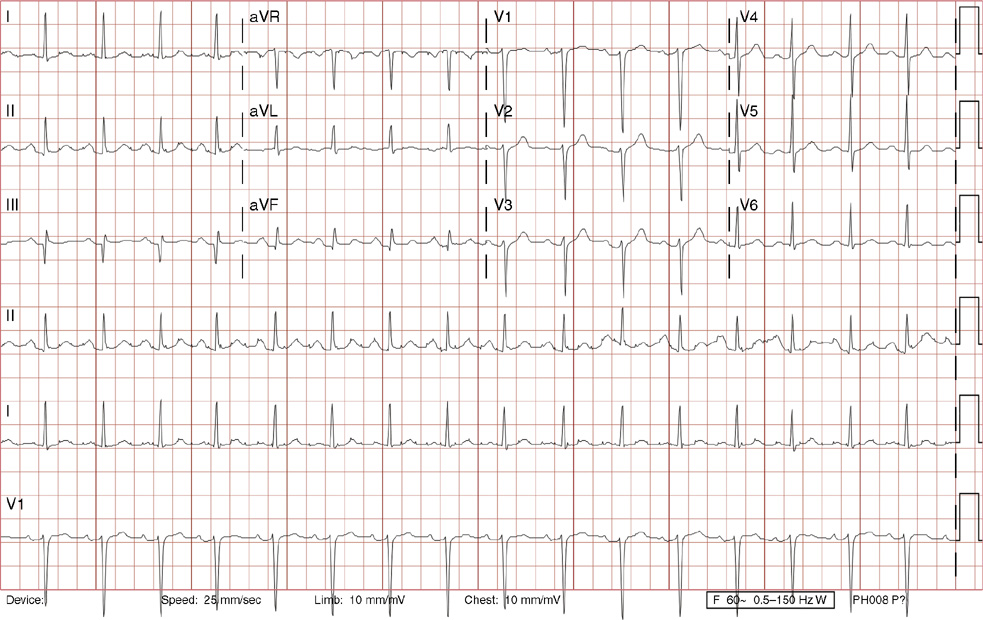



Ii Cardiology Radiology Key




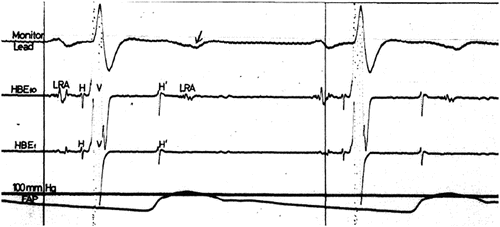
Atrioventricular Block And Pause Dependent Torsade De Pointes Heartrhythm Case Reports




Bradycardia An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
.png)



Float Nurse Various First Degree Heart Blocks




Atrioventricular Block Cardiovascular Disorders Msd Manual Professional Edition




Float Nurse Ekg Rhythm Quiz 236



Ecg A Pictorial Primer




First Degree Atrioventricular Block An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



First And Second Degree Atrioventricular Block Thoracic Key



Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Arrhythmias




Disorders Of Cardiac Rhythm Musculoskeletal Key




Evaluation And Treatment Of Av Block And Intraventricular Conduction Disturbances The Cardiology Advisor




References In Repetitive Nonreentrant Ventriculoatrial Synchrony An Underrecognized Cause Of Pacemaker Related Arrhythmia Heart Rhythm




Effectiveness Of Atrial Antitachycardia Pacing In The Treatment Of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation In Patients With Pacemakers Revista Portuguesa De Cardiologia English Edition




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog A Patient With A Ventricular Paced Rhythm And Chest Pain
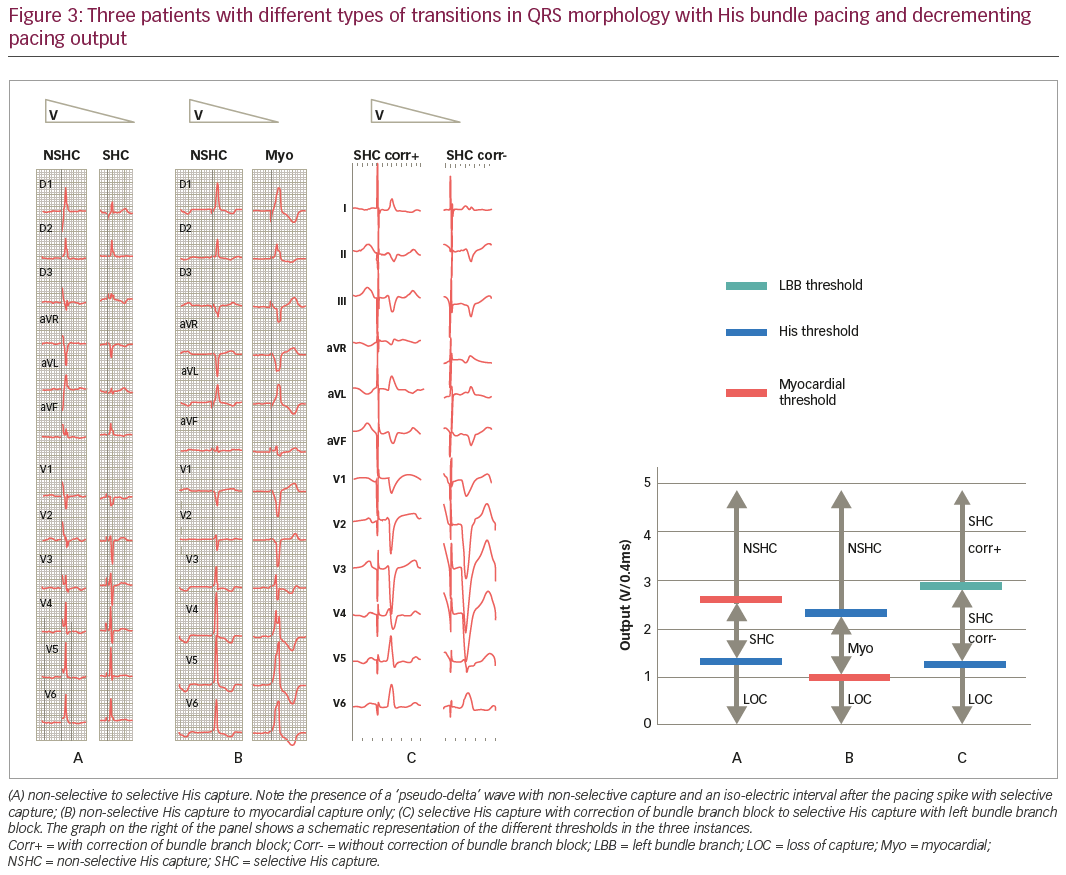



His Bundle Pacing Why Should You Be Doing It Touchcardio
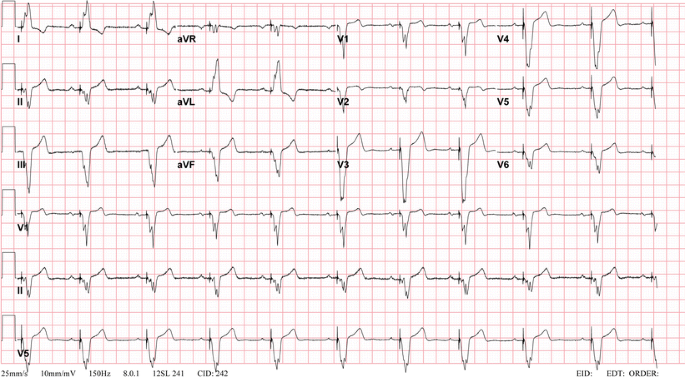



Congenital And Childhood Atrioventricular Blocks Pathophysiology And Contemporary Management Springerlink




His Bundle Pacing Is The Best Approach To Physiological Pacing Heart Rhythm O2




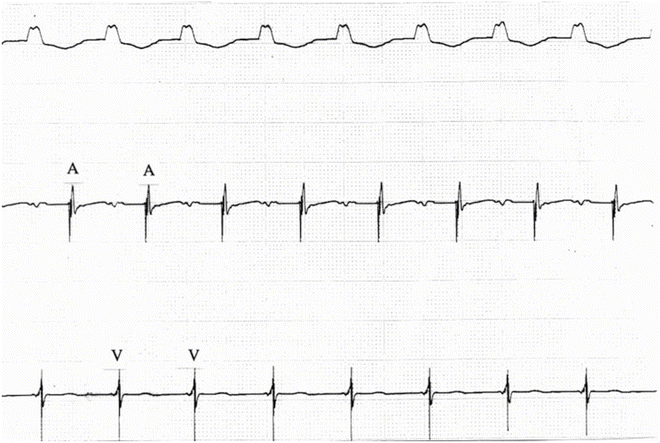
Atrial Sensed Ventricular Paced Rhythm After Av Nodal Ablation And Ppm Download Scientific Diagram




Differential Diagnosis Of Wide Qrs Complex Tachycardias The Cardiology Advisor




Indications And Recommendations For Pacemaker Therapy American Family Physician
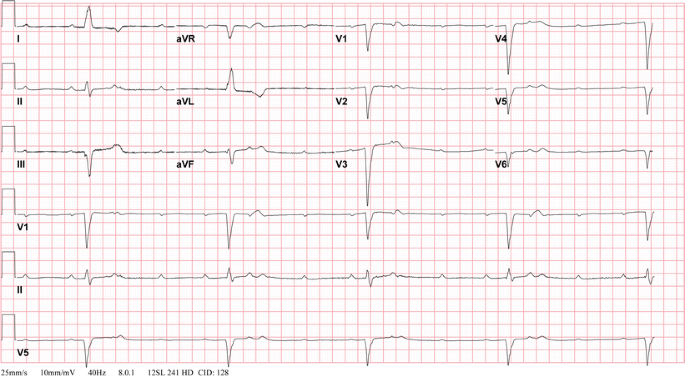



Congenital And Childhood Atrioventricular Blocks Pathophysiology And Contemporary Management Springerlink
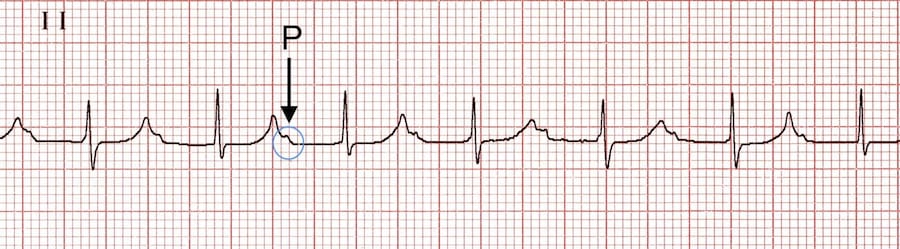



First Degree Heart Block Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Ecg Case 1 Question 3 Answer Learntheheart Com




Nclex Practice Questions Adult 3rd Degree Heart Block Physiological Adaptation Youtube
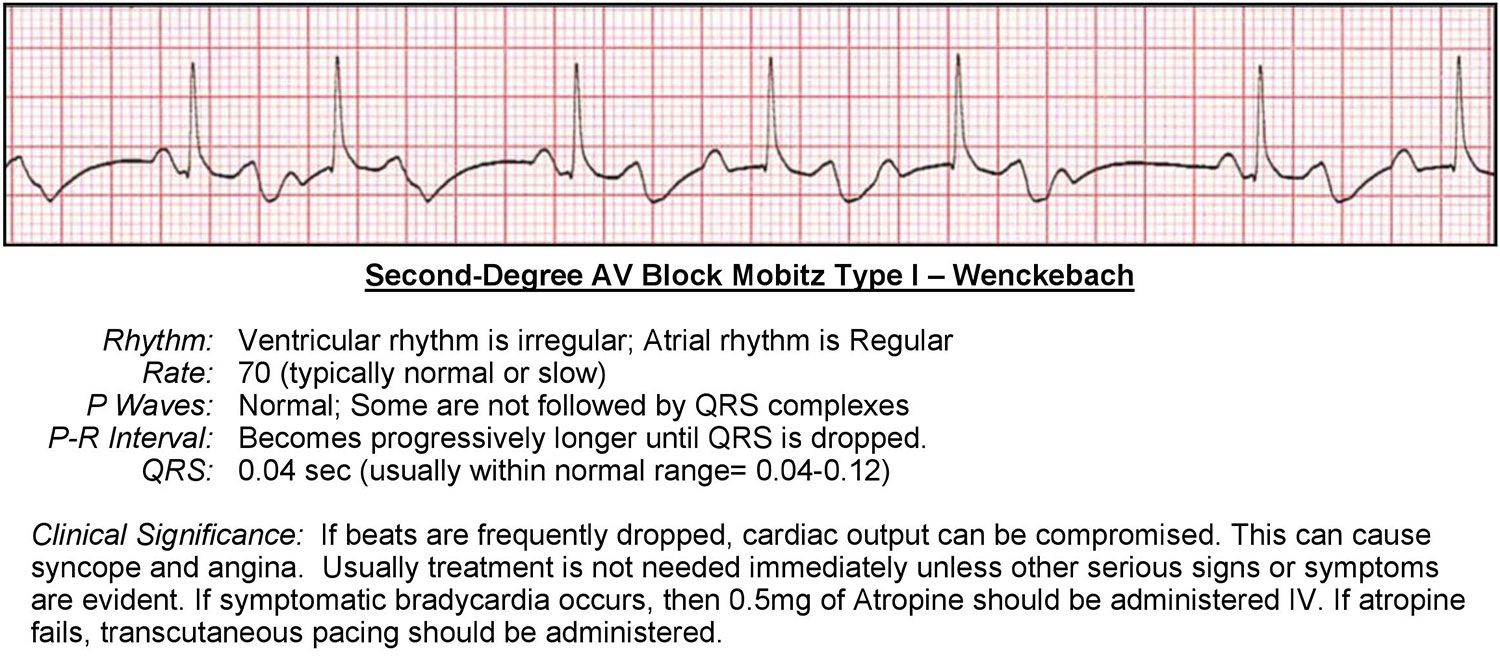



Atrioventricular Blocks Acls Wiki




Electrocardiographic Analysis For His Bundle Pacing At Implantation And Follow Up Sciencedirect
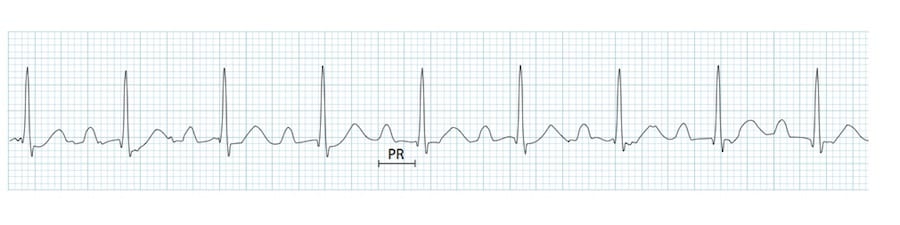



First Degree Heart Block Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Evaluation And Treatment Of Av Block And Intraventricular Conduction Disturbances The Cardiology Advisor
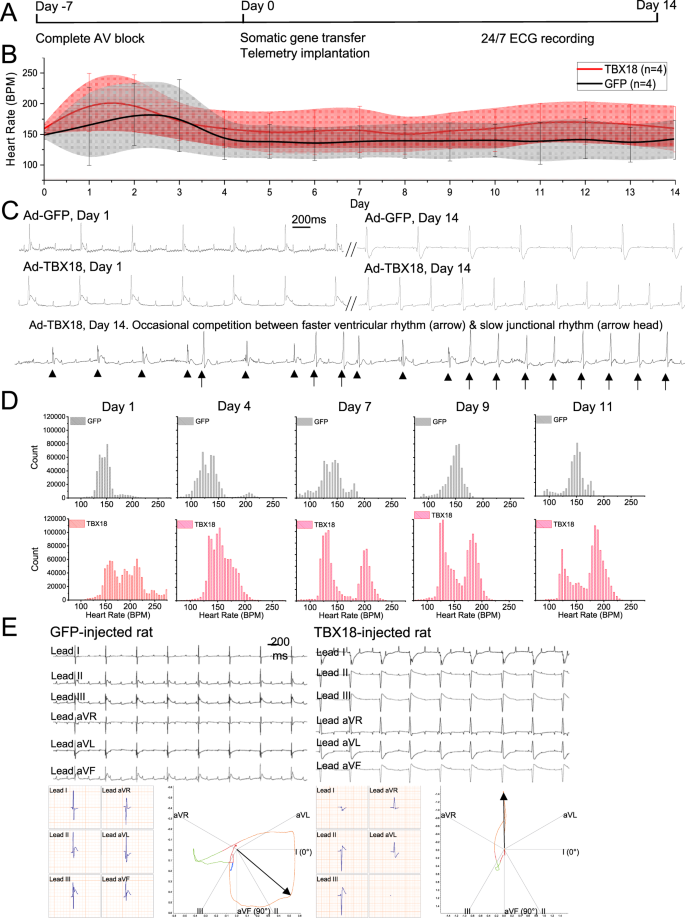



A Rat Model Of Complete Atrioventricular Block Recapitulates Clinical Indices Of Bradycardia And Provides A Platform To Test Disease Modifying Therapies Scientific Reports




Primary Ablation Of Atrial Flutter And Atrial Fibrillation Cardiology Clinics




Atrioventricular Block And Pause Dependent Torsade De Pointes Heartrhythm Case Reports



Year Old Male Cc Chest Pain Conclusion Ems 12 Lead



Www Heartrhythmcasereports Com Article S2214 0271 16 300 5 Pdf




Intracardiac Electrocardiograms Demonstrating Pacemaker Dependence Download Scientific Diagram


コメント
コメントを投稿